
As a result, investors can branch out from traditional funding routes to explore the latest developments in the digital economy. Here are a few examples of companies using blockchain to shake up the payments industry. There’s a lack of universally accepted blockchain standards in the accounting industry. This can create inconsistencies in how the technology is implemented and used across different firms.
- In some cases, transactions on a blockchain may be sufficient evidence for auditors to complete their assessments.
- Deloitte predicts that blockchain will become a “critical asset” for financial institutions.
- However, you can use permissioned (private) blockchains where only authorized users can access sensitive data.
- A blockchain is a distributed, peer-to-peer database that hosts a continuously growing number of transactions.
- Financial managers can track key performance indicators like liquidity ratios and cash flow metrics in real time, ensuring a current and accurate view of the business’s financial status.
- It is likely that many enterprises will try to harness this new technology and create value with it.
- Although the technology is rapidly evolving and will likely have an impact on accounting and auditing, some skepticism is warranted regarding potential benefits and ease of implementation.
Blockchain-Enabled Financial Reporting

This means that only the person assigned an address can reveal their identity. As Sales Forecasting a result, blockchain users can remain anonymous while preserving transparency. A blockchain allows the data in a database to be spread out among several network nodes—computers or devices running software for the blockchain—at various locations.
Benefits of Blockchain in Accounting

With blockchain employed, the entire process could (theoretically) be as fast as the click of a button. In order to protect user information and financial data, the chain encrypts each transaction on the network. All users have their own bookkeeping unique digital signature, used to verify a transaction between them and the entire chain.
Enhancing Security and Preventing Fraud with Blockchain
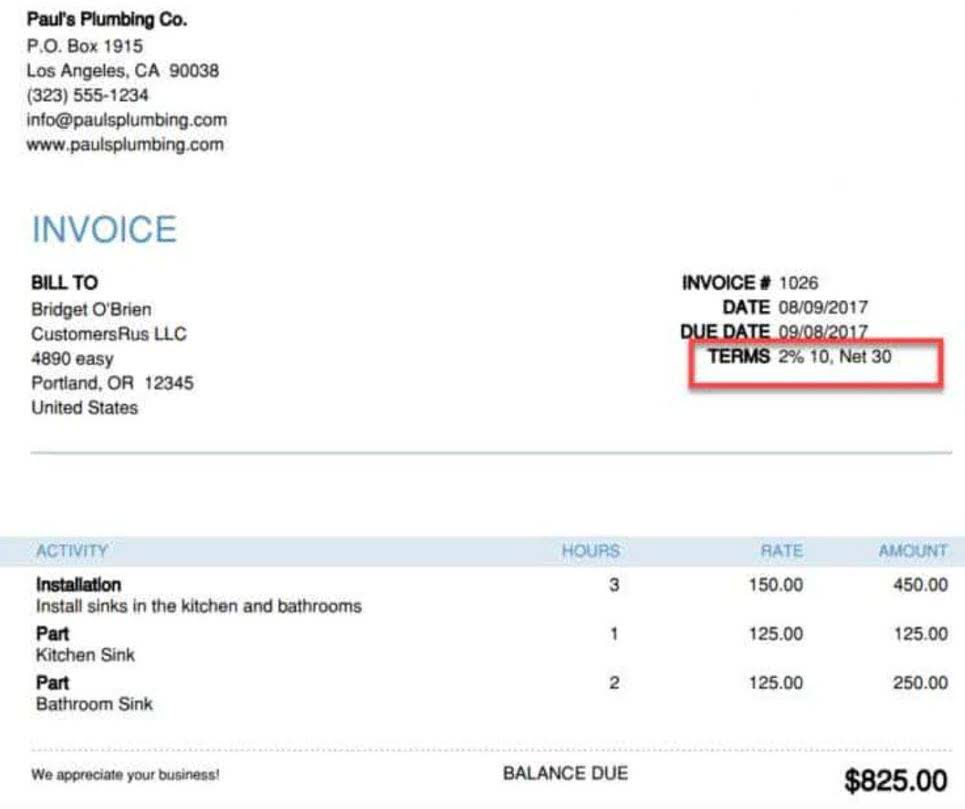
Firms must be prepared for the potential impact on their accounting processes. Smart contracts are transforming accounting by automating and streamlining financial operations. These digital agreements execute predefined terms without intermediaries, improving processes like payment releases, compliance checks, and reconciliations. In accounts payable, for example, smart contracts can trigger automatic payments upon receipt and verification of goods, reducing delays and administrative burdens.

- The technology’s decentralized nature ensures data security and integrity, protecting sensitive financial information.
- Blockchain’s potential in finance is vast, with key applications in cross-border payments, smart contracts, and security.
- A new and smaller chain might be susceptible to this kind of attack, but the attacker would need at least half of the computational power of the network (a 51% attack).
- Its transparent and tamper-proof ledger enhances the accuracy of financial data, reducing the risk of errors and fraud.
- The lack of consistent regulatory frameworks creates hesitation among fintechs, especially those operating across multiple jurisdictions.
- Recognized as a leading blockchain developer, Acropolium brings over 20 years of experience in custom software development, specializing in fintech solutions.
When predefined conditions are met, these contracts automatically execute actions, such as payments or agreement terms. For example, in accounting, a smart contract could be set up to trigger payments to suppliers once goods are delivered automatically, or to release funds once an invoice is verified. Consider a multinational retail company that sources goods from global suppliers. Each transaction—from purchasing raw materials to final delivery—is recorded on a blockchain ledger.

Enter blockchain, a technology blockchain in accounting that promises to address these issues and more, making it a perfect fit for the financial industry. Financial statement and CPA auditors sign off on a company’s financials when they believe, with reasonable assurance, that they are authentic and without fraud. That’s a vital stamp of approval that blockchain technology, in its current form, cannot give. An audit breaks down the entire company’s financials and gives it a stamp of approval.
